What's New in DataGrip 2025.3
Connection to cloud providers, introspection levels for Amazon Redshift, and more!
Connectivity
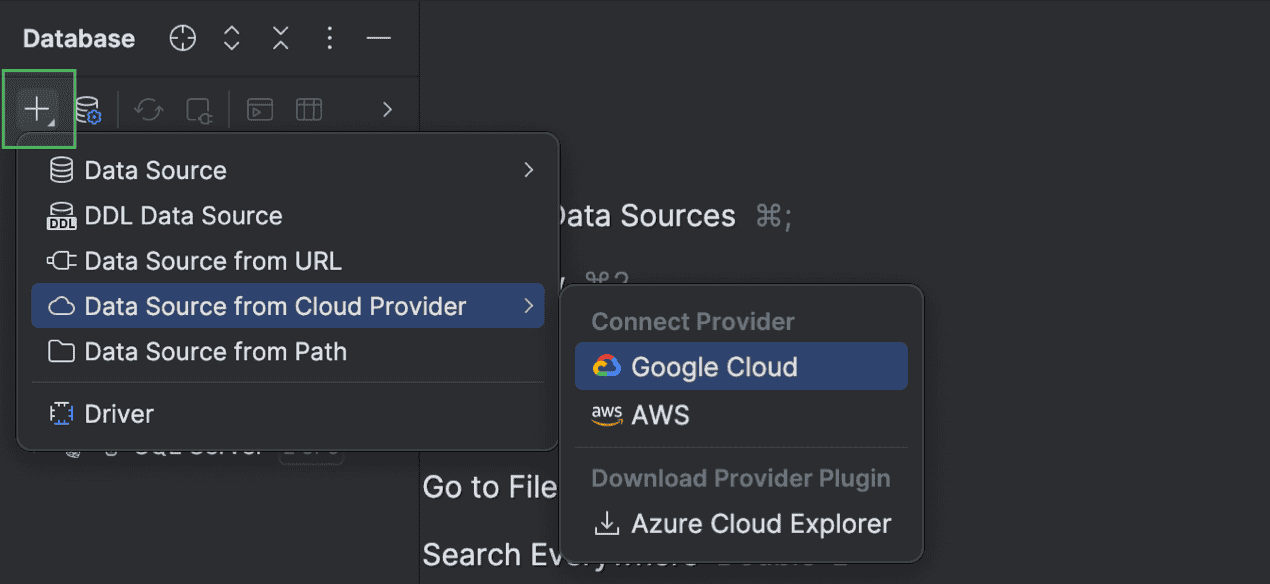
Connection to cloud providers
DataGrip now works with cloud database providers! In the new release, you can connect your AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud accounts to the IDE, browse the list of databases you have in those accounts, and choose the ones you'd like to connect to. DataGrip will create new data sources and fill in all connection details.
To connect to your cloud account, click New | Data Source from Cloud Provider and select your cloud provider.
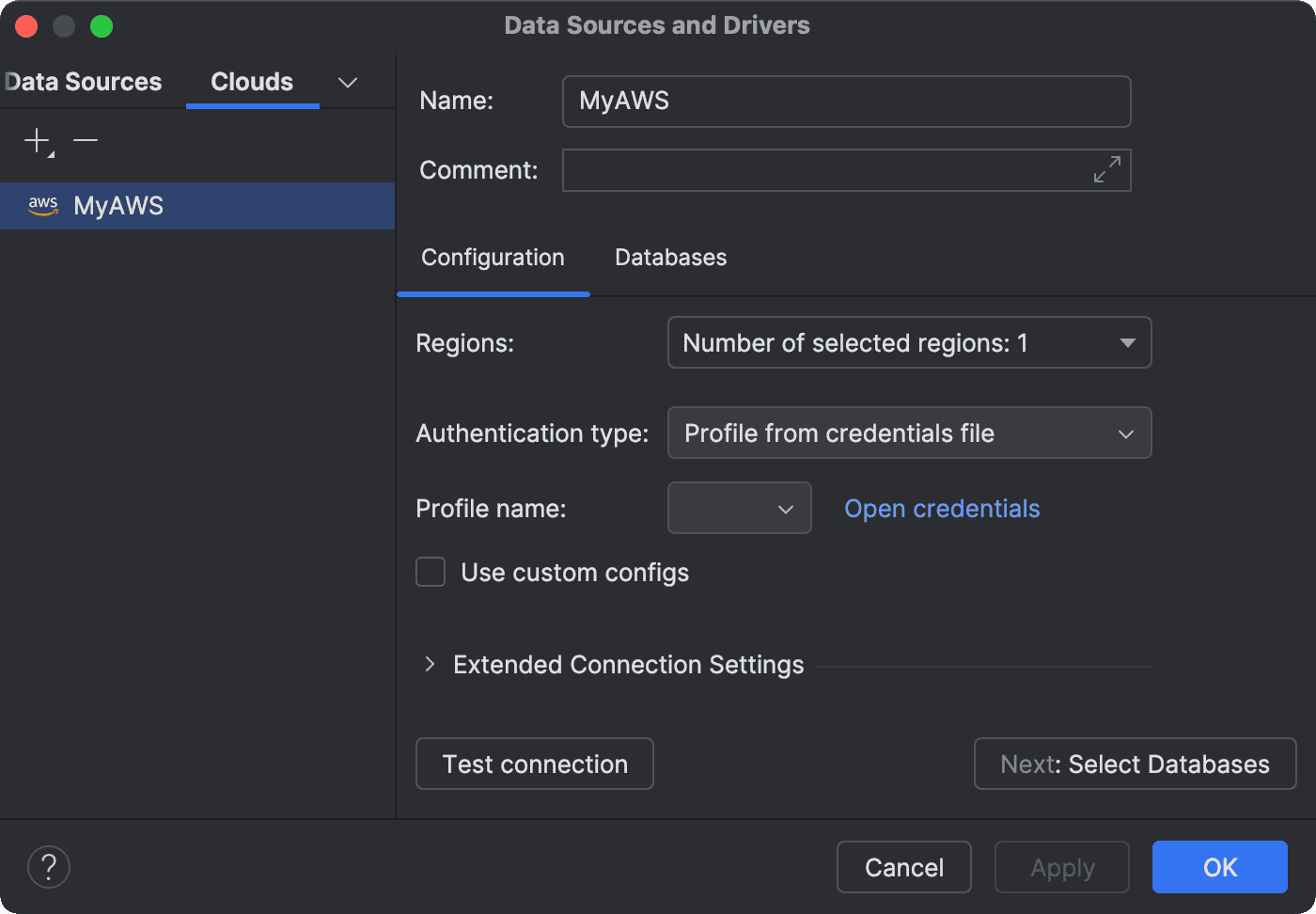
All of the cloud accounts connected to your IDE are displayed on the Clouds tab of the Data Sources and Drivers dialog.
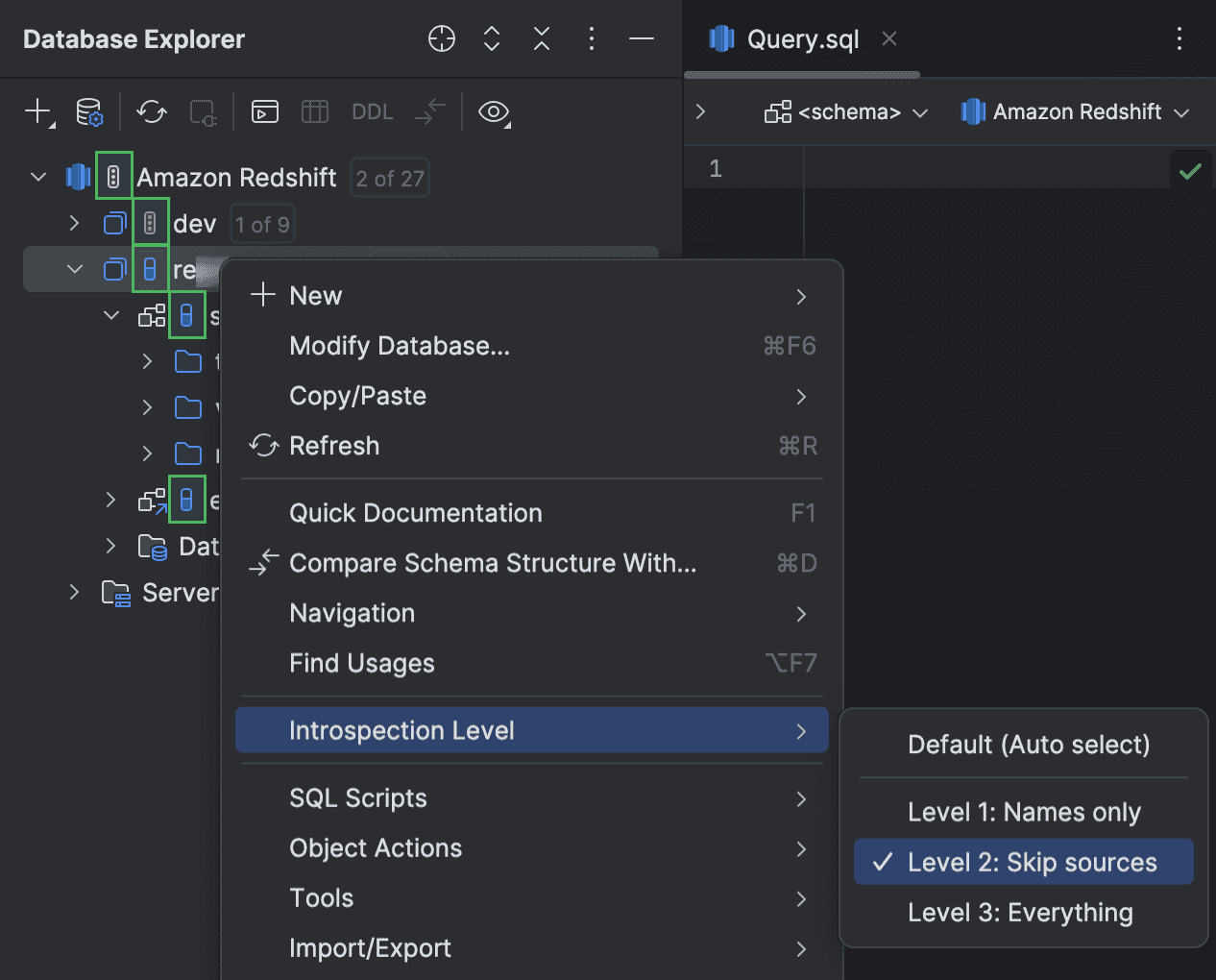
Introspection levels Amazon Redshift
This release adds the introspection levels feature to DataGrip's Amazon Redshift functionality. With this feature, DataGrip automatically adjusts the amount of metadata loaded for a database based on its size, which can save you a significant amount of time because you don't have to worry about large databases slowing things down. You can also select a different introspection level for each schema based on your task requirements.
Redesigned folders in the database explorer
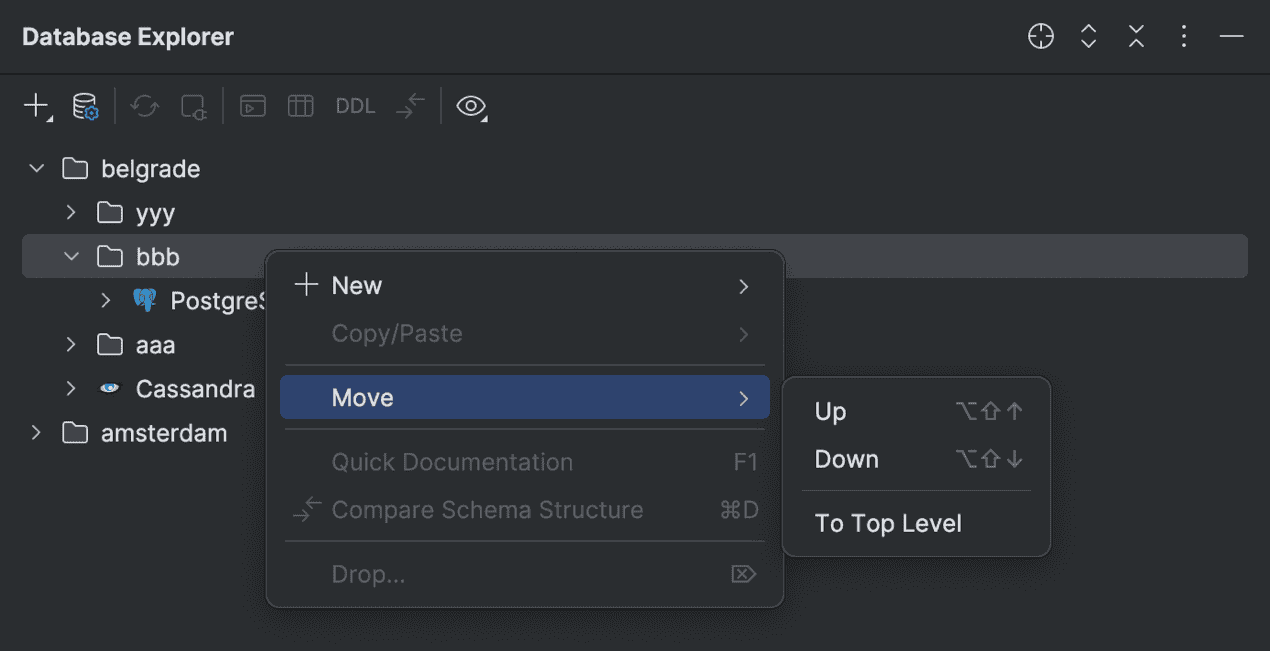
We have redesigned the folders that are used in the
database explorer.
Previously, they were virtual and were not stored anywhere. Since these folders are essentially groups, but not directories, their configuration information is now stored in .idea/db-forest-config.xml. Any folders you already have will be automatically converted to the new configuration.
In the database explorer, you can arrange your folders and data sources in any way that works for you, as they are not sorted alphabetically. To do this, use the Move context menu action group or the corresponding shortcuts.
In addition, you can now create empty folders. To create a new folder at the highest level, click New on the toolbar and select Folder. To create a new subfolder, select New | Folder in the context menu of the higher-level folder.
Explain Plan
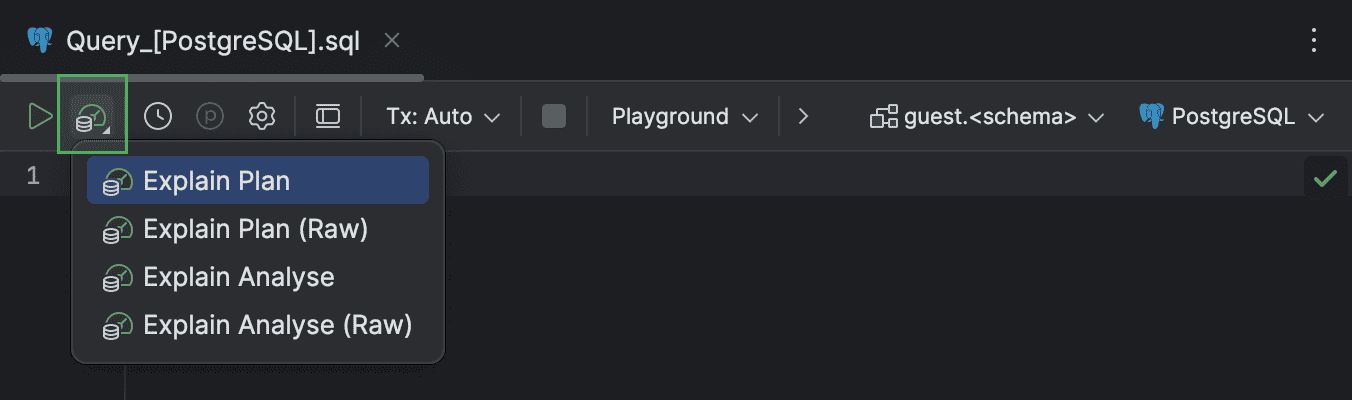
Query file toolbar button
We have made the Explain Plan actions more accessible. Now you can click the Explain Plan button right on the query file toolbar to access them.
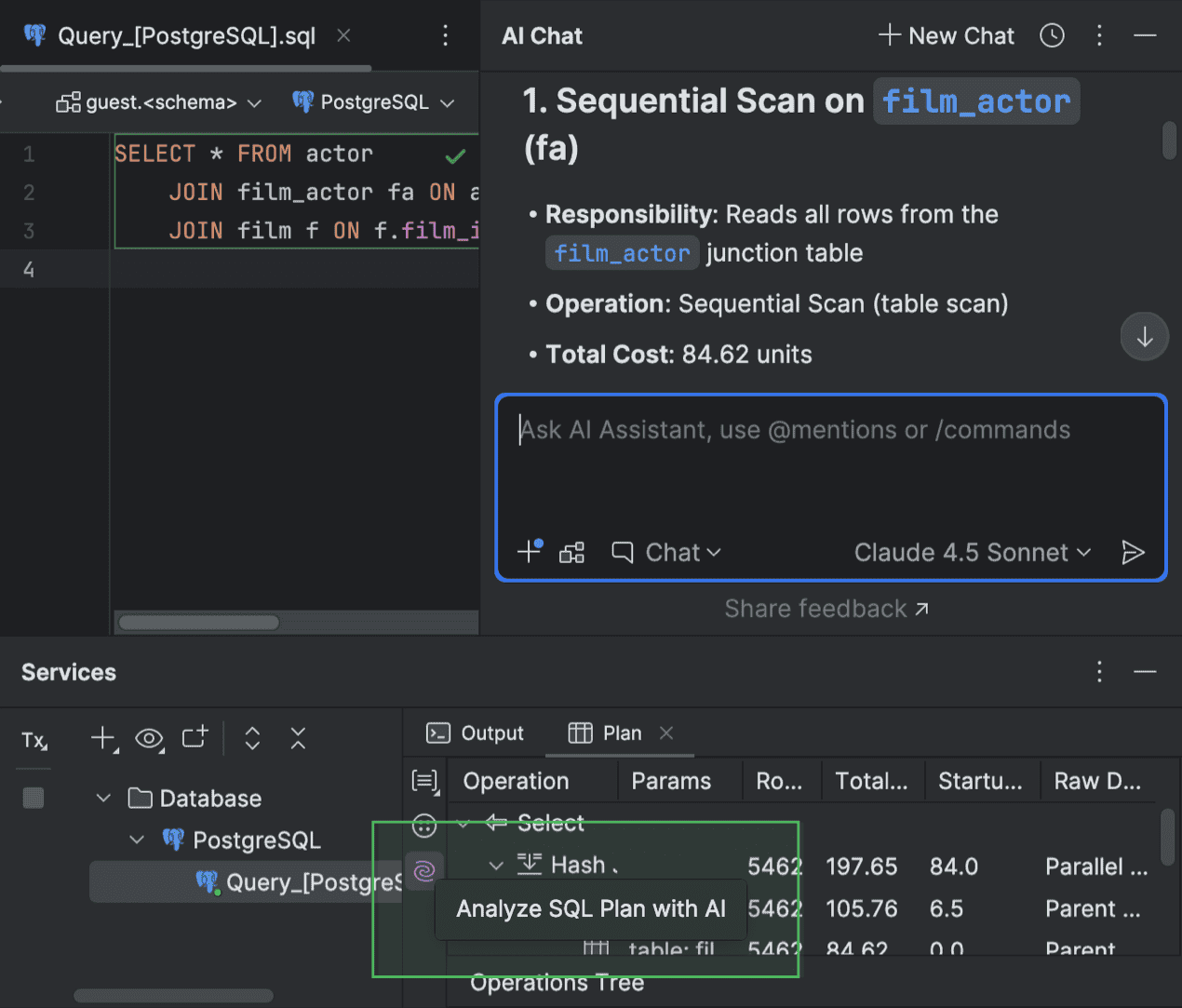
Explanation for query plans AI Assistant
For a query execution plan, you can ask AI Assistant to explain it when viewing it in the Plan tab of the Services tool window. To do this, click Analyze SQL Plan with AI on the left toolbar of the tab. AI Assistant will then provide an explanation in the chat, where you can ask any additional questions about the plan.
To use this feature, you need to have the AI Assistant plugin installed in your IDE.
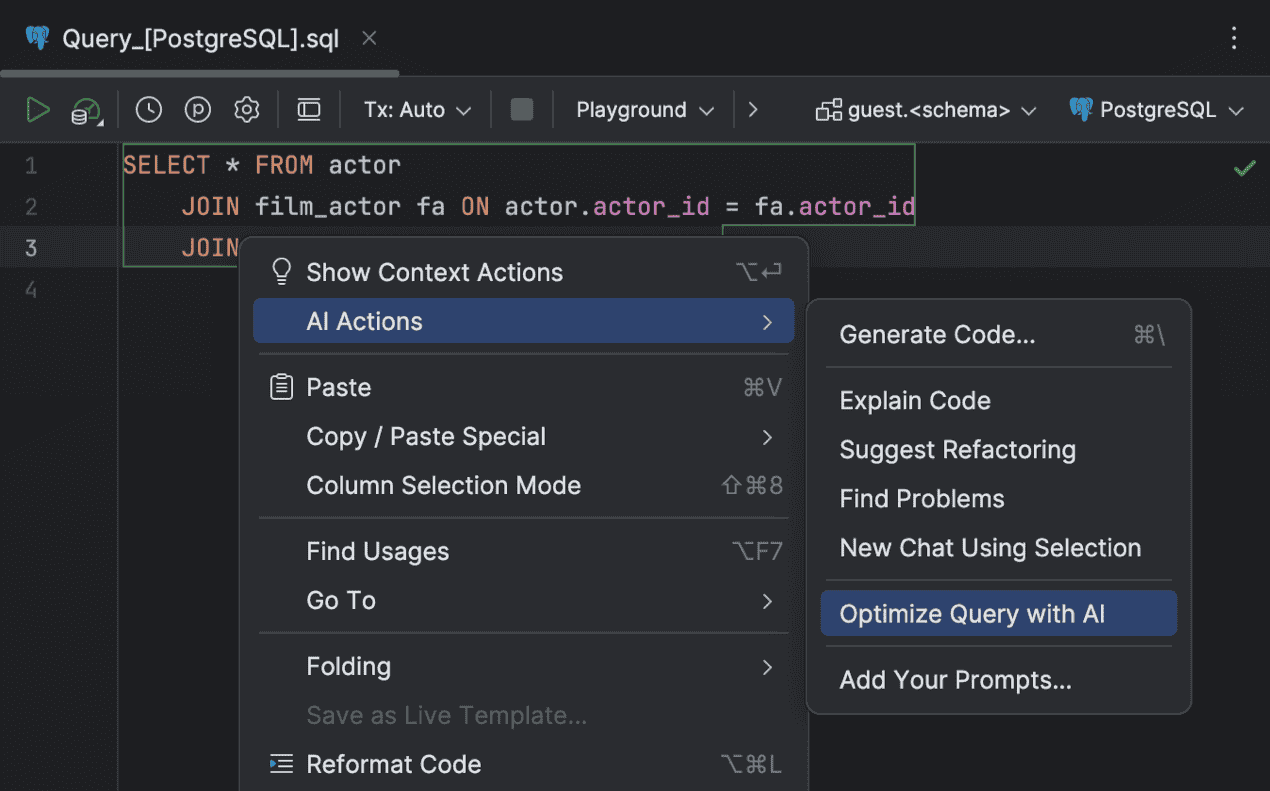
Query optimization AI Assistant
AI Assistant can now optimize your query for better performance and efficiency. It does this by:
- Automatically detecting inefficiencies such as redundant
JOINclauses, missing indexes, or suboptimal execution plans. - Providing actionable suggestions or automatically rewriting queries to improve performance.
- Leveraging Explain Plan outputs for deeper analysis and diagnostics.
You can ask AI Assistant to optimize your query by right-clicking it and selecting AI Actions | Optimize Query with AI. AI Assistant will then give you a list of suggestions in the chat, and you can continue to ask any questions there.
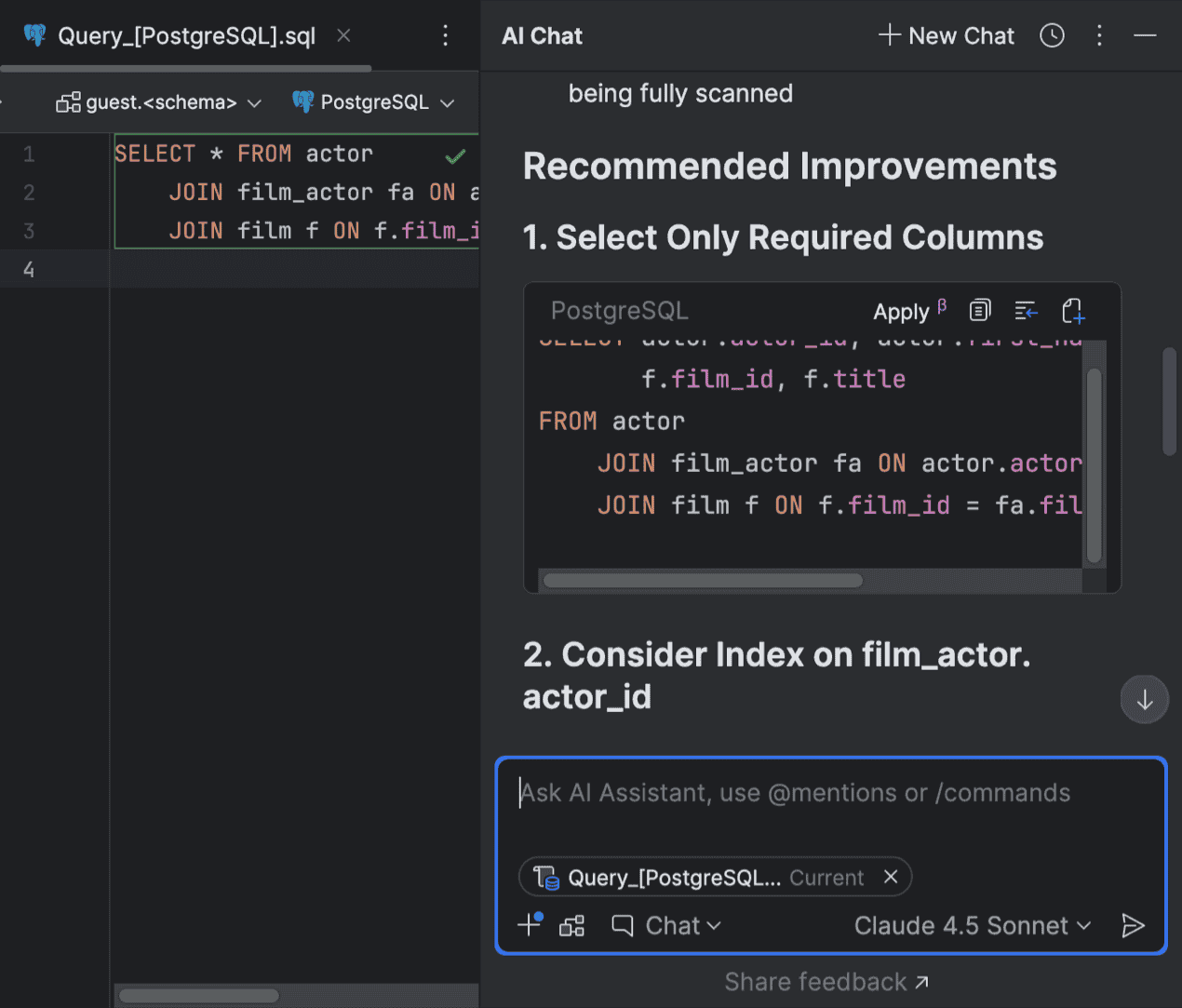
To use the AI Assistant query optimization feature, you need to have the AI Assistant plugin installed in your IDE. This feature may require you to attach the database schema so that it can suggest proper optimizations.
Code editor
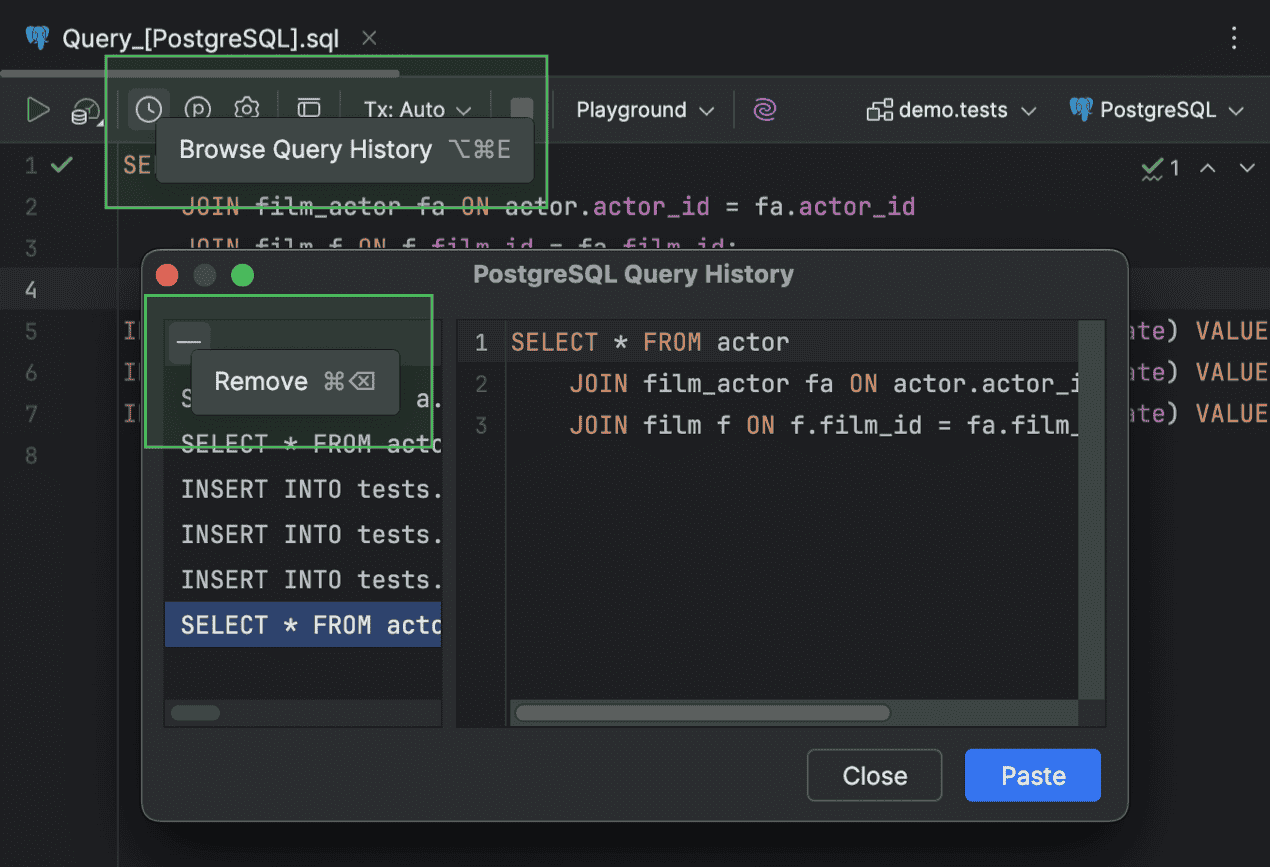
An action to remove history records from Browse Query History
Now, you can delete query history records that DataGrip stores and displays in the Query History dialog. To do this, open the dialog by clicking Browse Query History on the query file toolbar. From the list of executed queries, select the one you want to delete and click Remove.
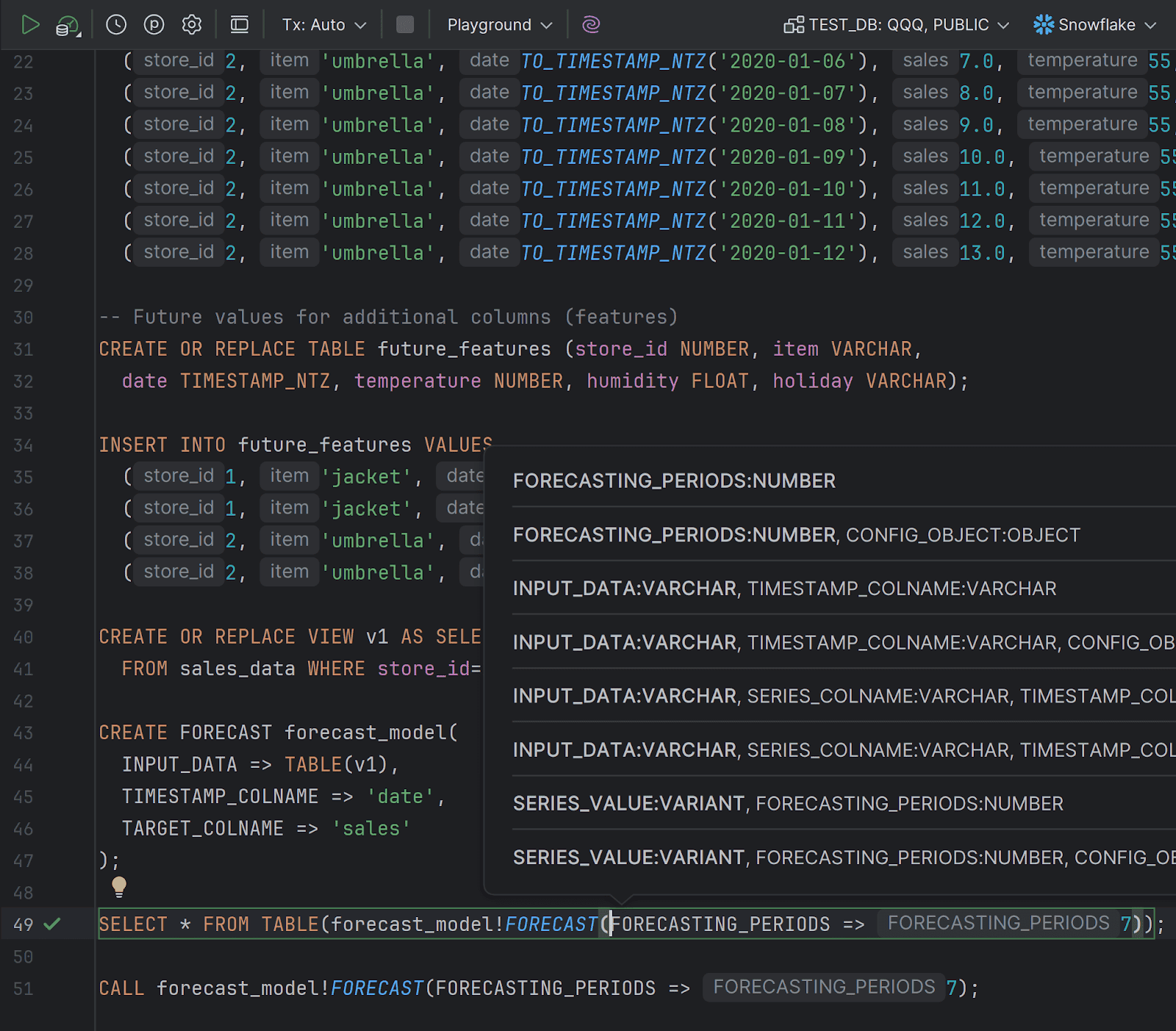
Support for classes Snowflake
Snowflake database functionality now supports classes, including the following:
- Introspection of built-in classes and methods, as well as class instances.
- Parsing of DDL statements for class instances, related
SHOWstatements, and method calls. - Resolution of references to classes, class instances, and methods.
- Parameter info and signature inspection for method calls.
Working with data
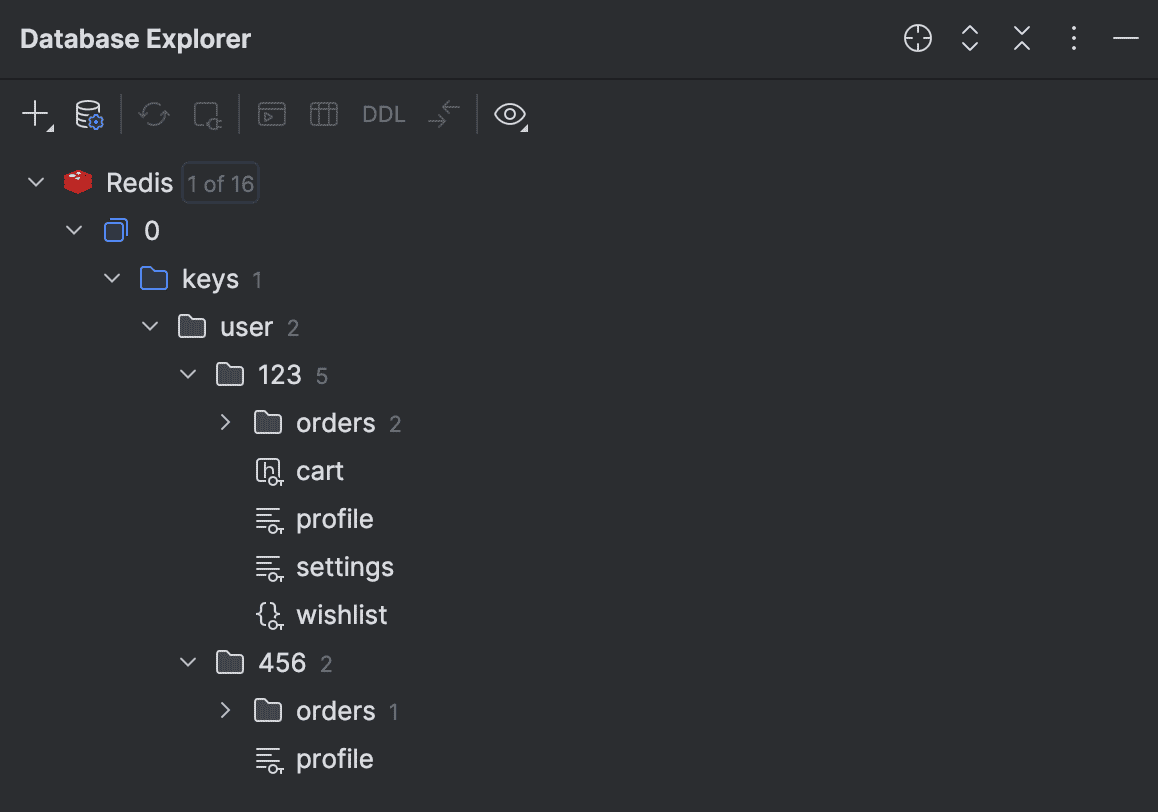
Keys of different types in one group Redis
We've added support for hierarchical
Redis
keys. Now, you can specify a separator, like :: or :, and keys will be displayed in the
database explorer
using a directory structure. For keys with names like user::<segment_01>::<segment_02>, the view is as follows:
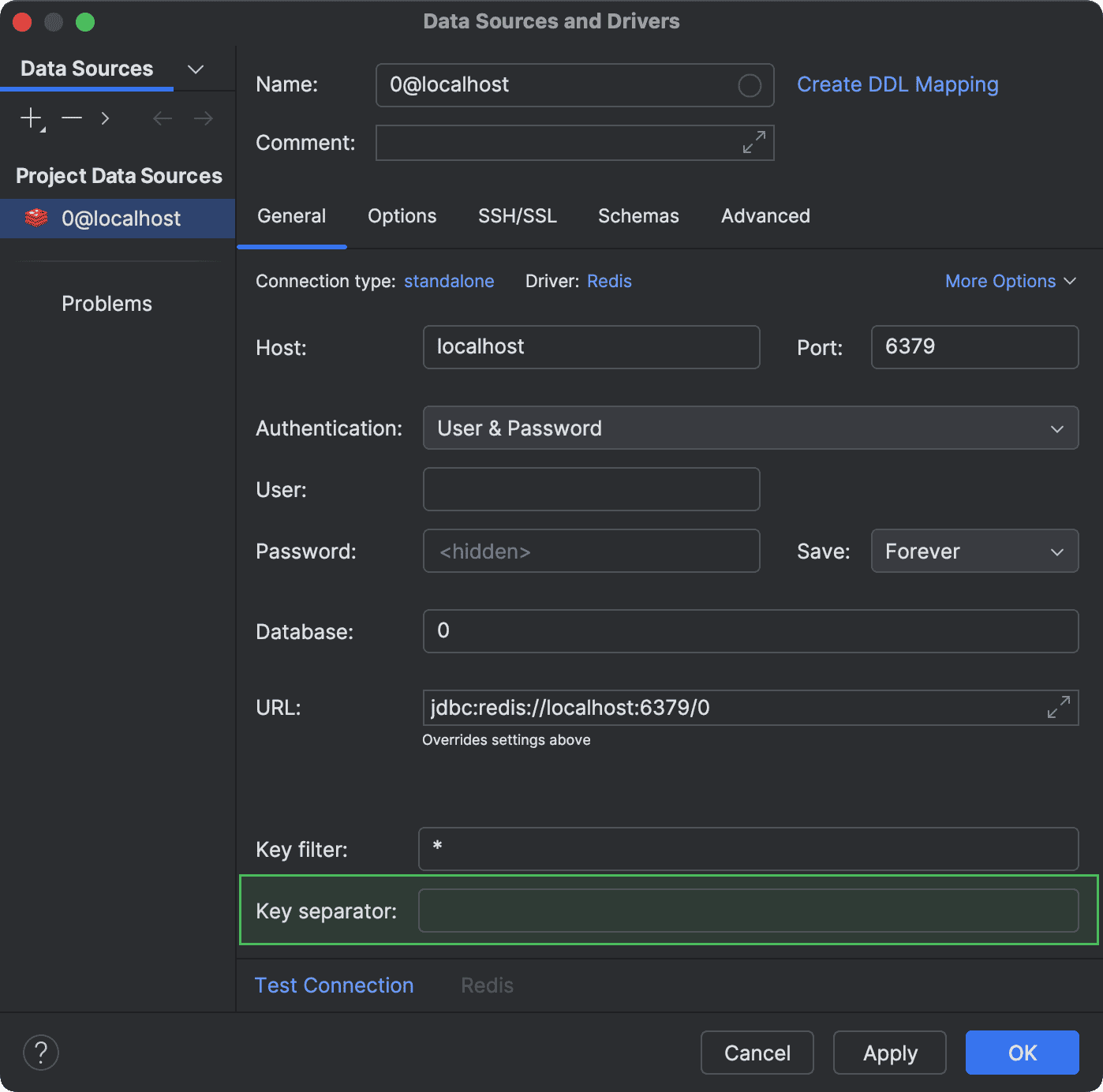
To enable this view, specify a key separator on the General tab of the Data Sources and Drivers dialog.
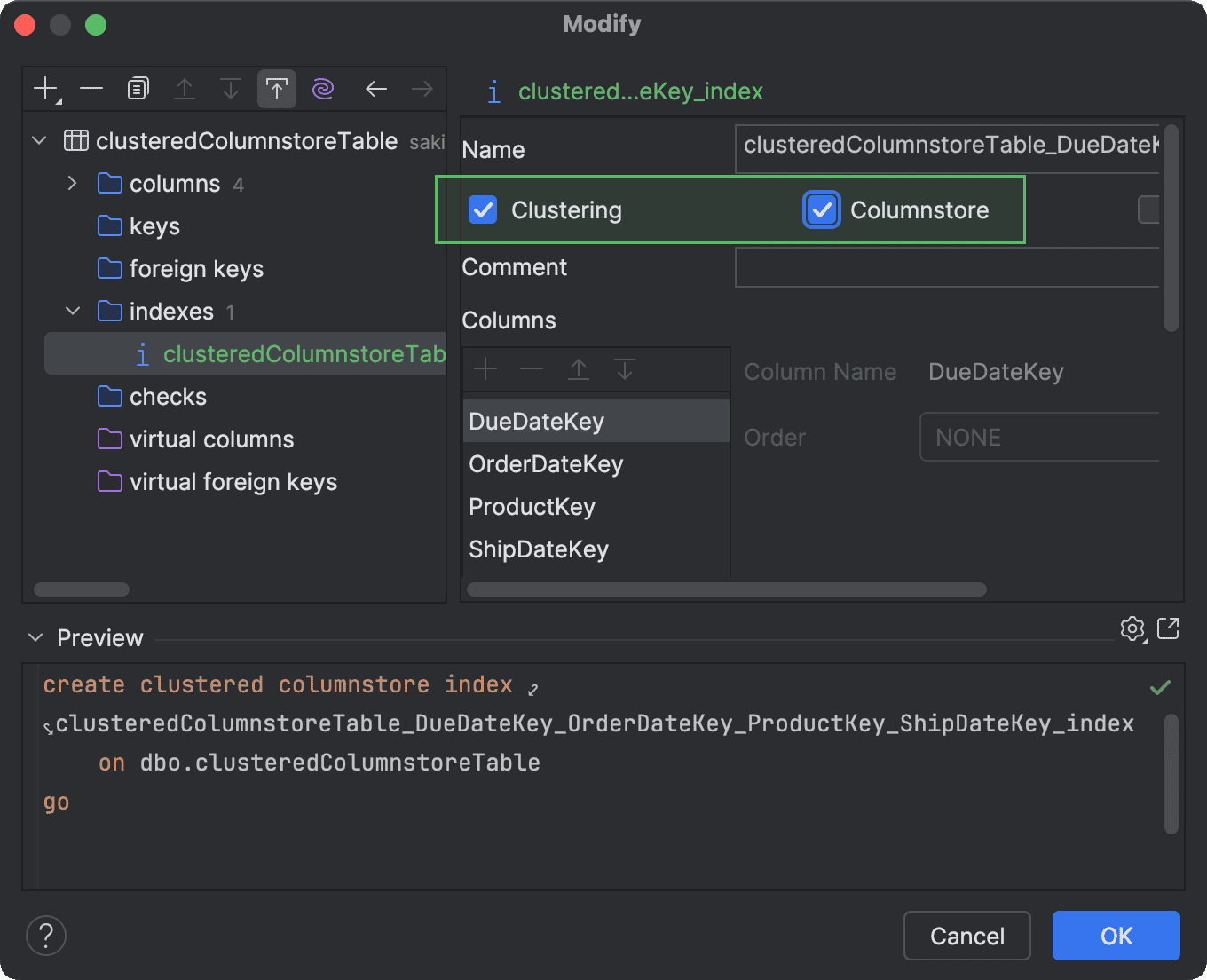
Clustered and nonclustered columnstore indexes support Microsoft SQL Server
DataGrip now supports creating and modifying clustered and nonclustered columnstore indexes for Microsoft SQL Server. You can work with them in code generation and also use the indexes in the Create and Modify dialogs.
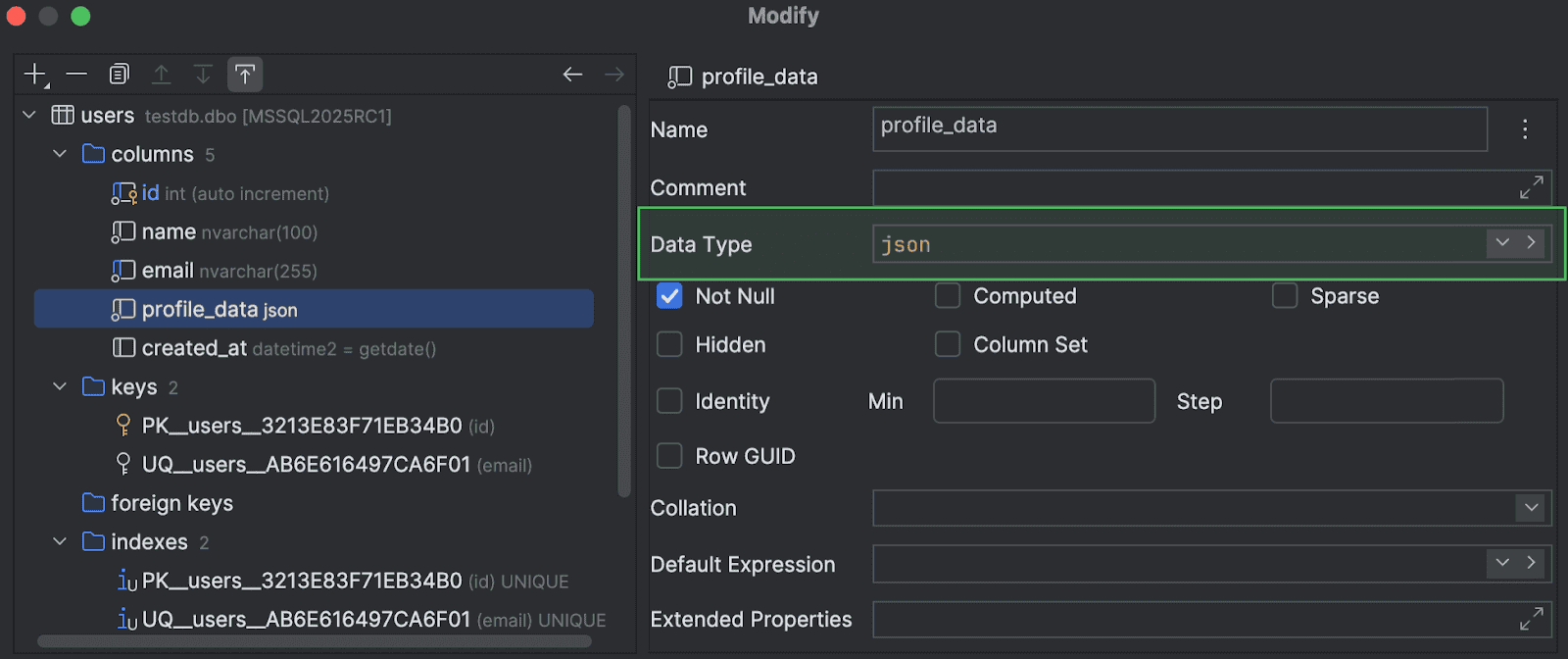
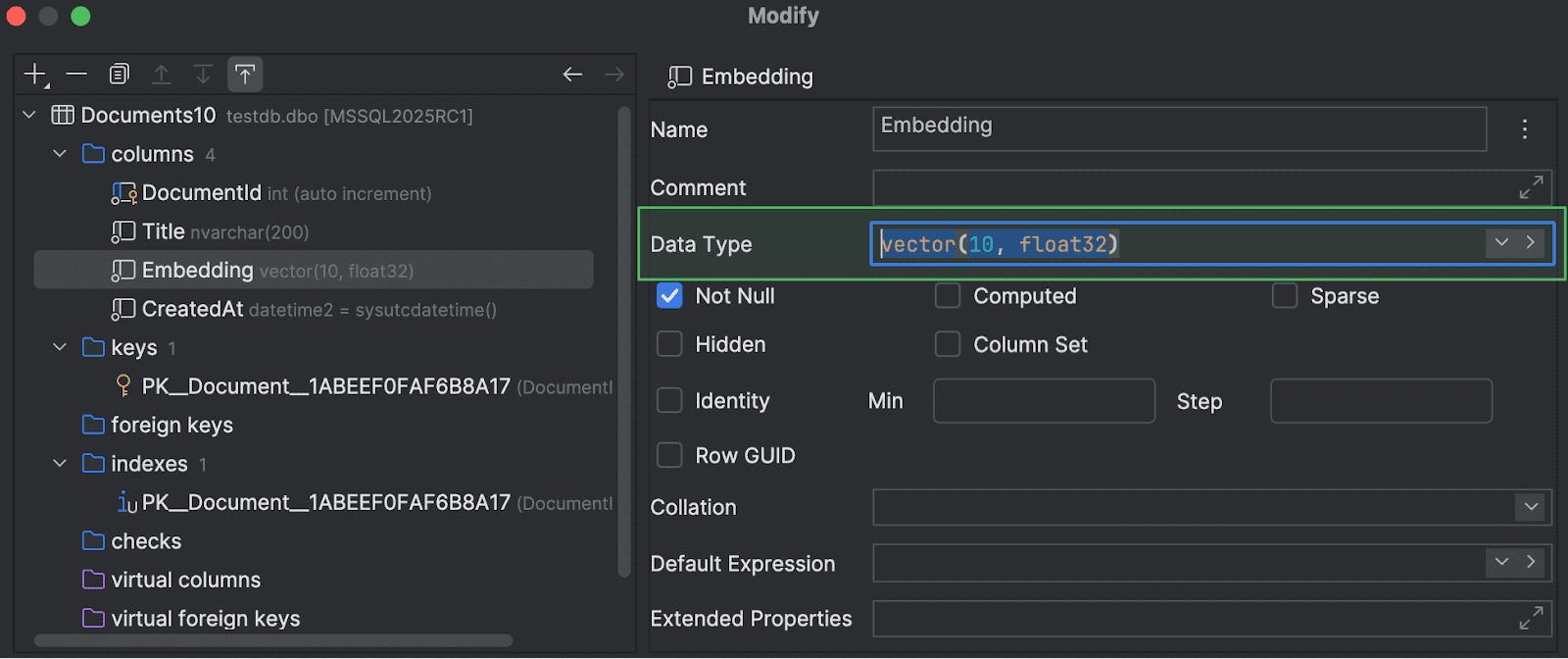
Support for VECTOR and JSON data types
Microsoft SQL Server
We've also added support for the
VECTOR
and
JSON
data types that were introduced to Microsoft SQL Server 2025 earlier this year. These data types are now available in code completion suggestions, where they are highlighted properly, and you can also use them in the
Create and Modify dialogs.
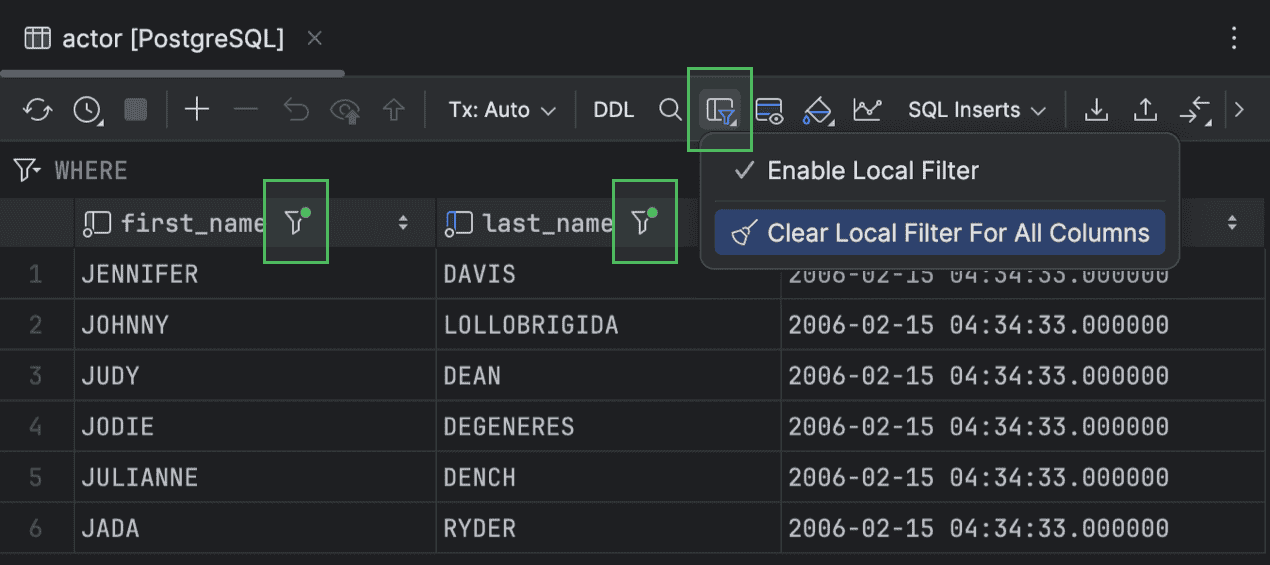
Toolbar action for clearing all local filters in a grid
We've added the local filters clearing action to the data editor toolbar. Now, you can clear the local filters for all columns in your grid by clicking Table Result Local Filter and selecting Clear Local Filter For All Columns.
UI and UX improvements
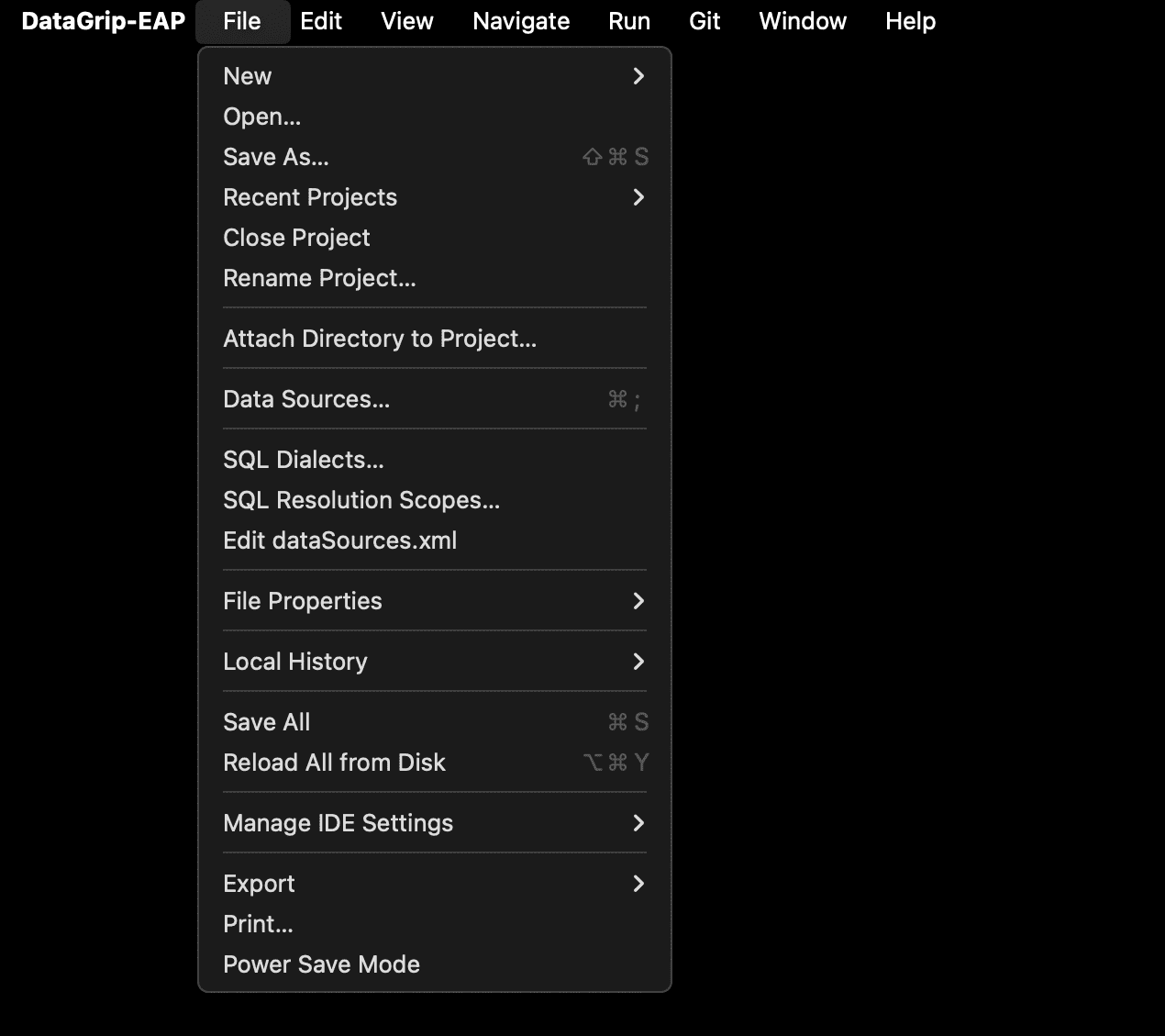
Main menu redesign
We have restructured and improved the main menu by clearing out some of the clutter and keeping only the most useful actions, such as Reformat Code, Recent Changes, Jump to Query File, and Run Current File. Now it is easier to find and invoke the actions you need most frequently.
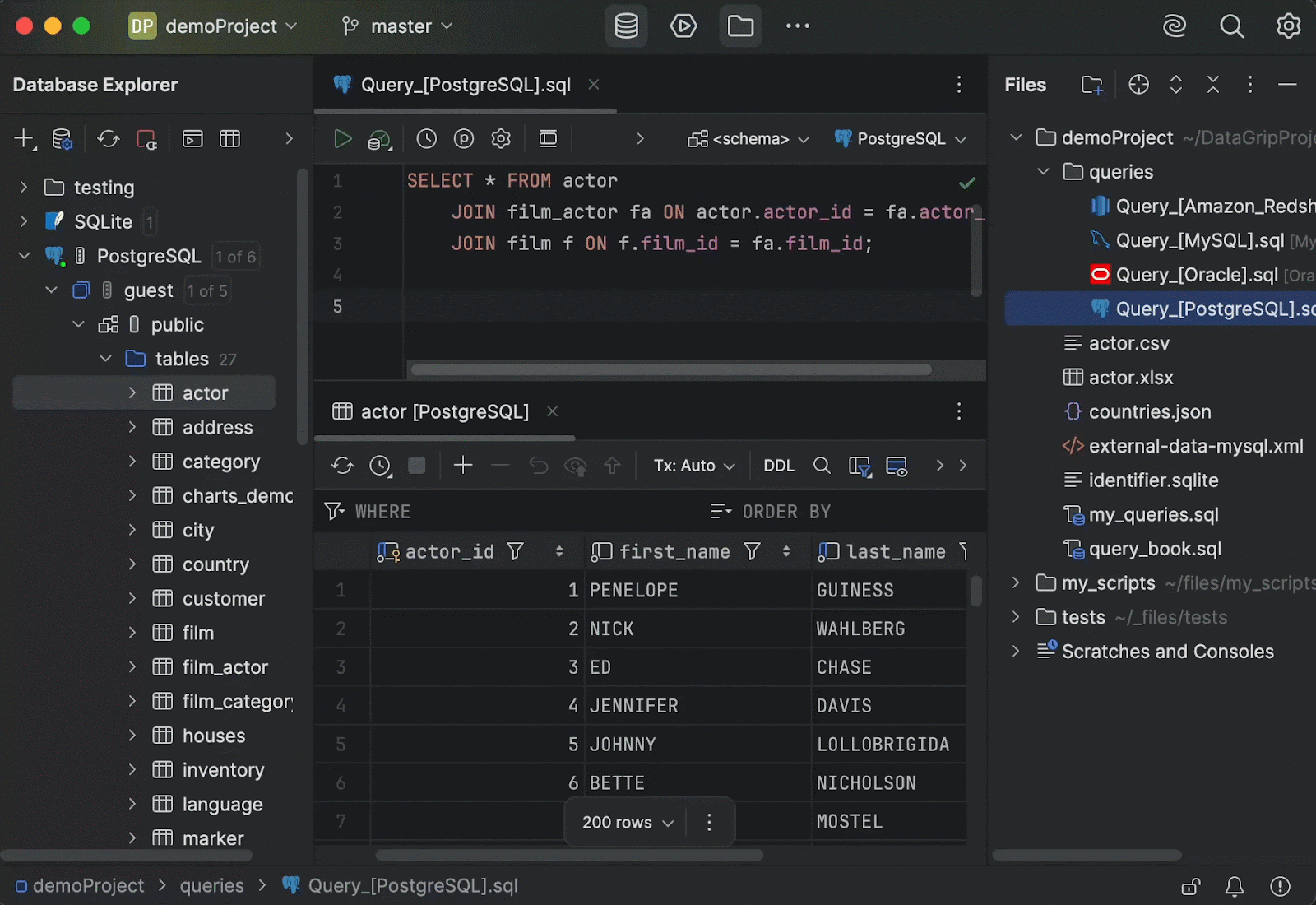
Islands theme becomes the default
DataGrip now uses the new Islands interface theme by default. The theme is available in both dark and light modes. This update is a visual refresh only, meaning that all functionality will remain the same.
To turn the new theme on or off, open the IDE Settings dialog and navigate to the Appearance & Behavior | Appearance settings page.
We hope you enjoy these updates! If you come across a bug or would like to submit a feature suggestion, please do so via DataGrip's issue tracker.
Want to stay up to date on the latest features and receive tips on how to work with databases more productively? Subscribe to DataGrip's blog and follow us on X!